What is Rocket Propulsion?

This article will review the basic characteristics of rocket propulsion, including the application of Newton’s Third Law of Motion, types of propellants, forces acting on rockets during flight, and more.
A rocket is an object that is propelled by the ejection of expanding gases that have been generated from propellants, and that does not depend upon external sources. The engine contains its own propellant and obtains forward motion by reactive propulsion. Propulsion is obtained by the ignition of the propellant, whereby the energy of explosion offers an opposite thrust that causes acceleration. Oxygen available in the atmosphere functions as the oxidizer for the fuel. Gases at an extremely high temperature are produced by combustion of solid, liquid, or gaseous fuel in a combustion chamber. These gases pass through a nozzle, and thermal energy is converted into kinetic energy, causing acceleration.
Parts of a Rocket
A rocket is comprised of the following parts:
○ Rocket engines and nozzle
○ Propellant

○ Propellant tank
○ Directional stabilization and navigational devices
○ Structure to hold the parts
○ Wings
○ Rocket tube or shell that covers and streamlines the rocket
Theory of Operation of Rockets
Propellants in the categories of gas, solid, liquid or a mixture of solid and liquid are used in rocket engines. A chemical reaction occurs in the combustion chamber between the fuel and oxidizer. The hot gases accelerate out from the rear of the rocket, causing thrust in the combustion chamber and producing propulsion on the principles of Newton�s Third Law. When the propellant is exhausted rearwards at a high speed, the rocket is propelled forward due to rocket thrust.
Rocket Propellants
The rate of flow of propellants is varied during a flight to control the thrust and speed of the vehicle and to minimize aerodynamic losses. Rocket propellants are of the following types:
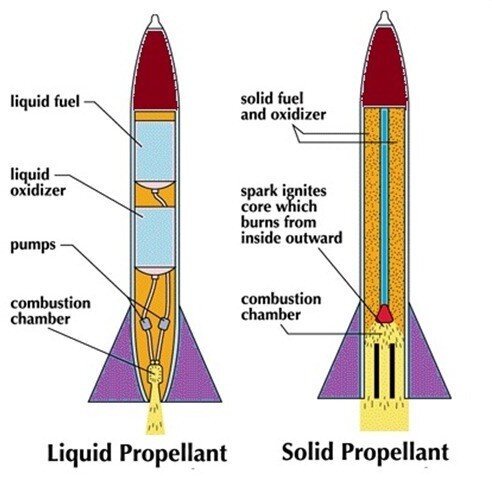
Solid Propellant: Oxidizers is included in the fuel. It is simple and safe to manage the fuel. However, the combustion cannot be blocked after ignition of fuel.
Liquid Propellant: Liquid fuel and liquid oxidizer are utilized. During pre-launch, liquid fuel burns gradually until release of the oxidizer, producing sudden fast burning and adequate force for lifting. Regulation of fuel and oxygen supplies can control the rockets.
Hybrid Propulsion: Solid fuel and liquid oxidizer are employed. The solid fuel, when combined with liquid oxidizer, burns quickly. Thrust of the rocket can be varied by controlling the supply of oxygen.
Nuclear Propulsion: Nuclear energy is utilized for superheating of hydrogen gas, when it leaves the rocket at an extremely high speed. However, safety factors must be considered thoroughly while using nuclear energy.
Advanced Rocket Propulsion Concepts
○ Fusion Rocket Propulsion: Plasma at a high temperature from a fusion reactor is utilized as exhaust from the rocket. This technology is under active research.
○ Antimatter Catalyzed Nuclear Pulsed Propulsion: An extremely interesting and expensive proposal, still being researched. Nuclear pulse propulsion is a technique of propulsion that utilizes nuclear explosions to produce thrust. The capacity of the engine depends upon the size of the nuclear bombs necessary to produce thrust. Making these bombs in small ranges is difficult, and a heavy spacecraft structure is required for larger bombs. Antimatter catalyzed nuclear pulse propulsion is a form of a nuclear pulse propulsion that involves utilization of antimatter as a catalyst in nuclear reactions. By injecting slight antimatter into fuel, fission of the fuel is obtained. Use of antimatter spacecraft are planned to reduce fuel costs significantly.
Forces Acting on a Rocket
During flight, the following major forces act on the rocket:
○ Thrust of the engine
○ Lift
○ Aerodynamic drag that decides the minimum strength of the vehicle to prevent buckling.